

The structures are similar because they were meant to perform the same functions, and these structures aren't inherited from a common ancestor.įor example, bats and birds have the same wing structure, but birds are closely related to animals, and bats are not. The functions of every organism are different from others.Īnalogous structures are found in unrelated organisms with similar body structures. One example of homologous structures can be the forelimbs of humans, animals, dolphins, rodents, bats. Such body structures are termed homologous structures.

But the descendants use these structures differently.
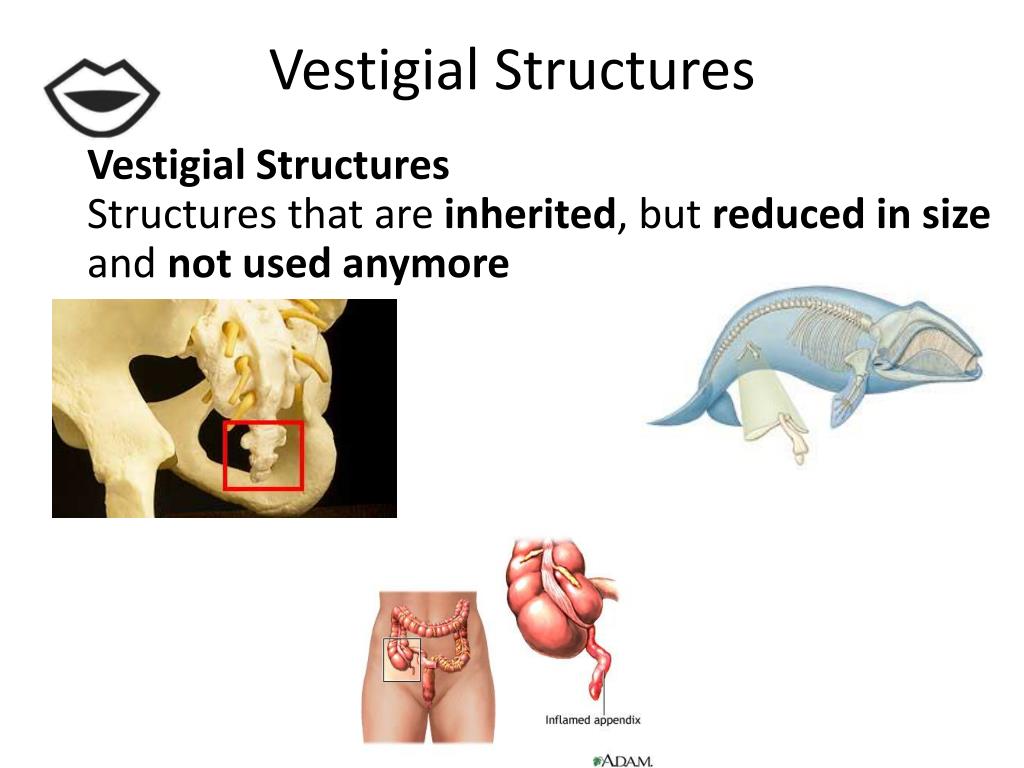
These structures are the same because they must've inherited them from a common ancestor. Some related organisms have similar structures in some parts of their body structure. These structures will help you understand “ how comparative anatomy provides evidence for evolution.”
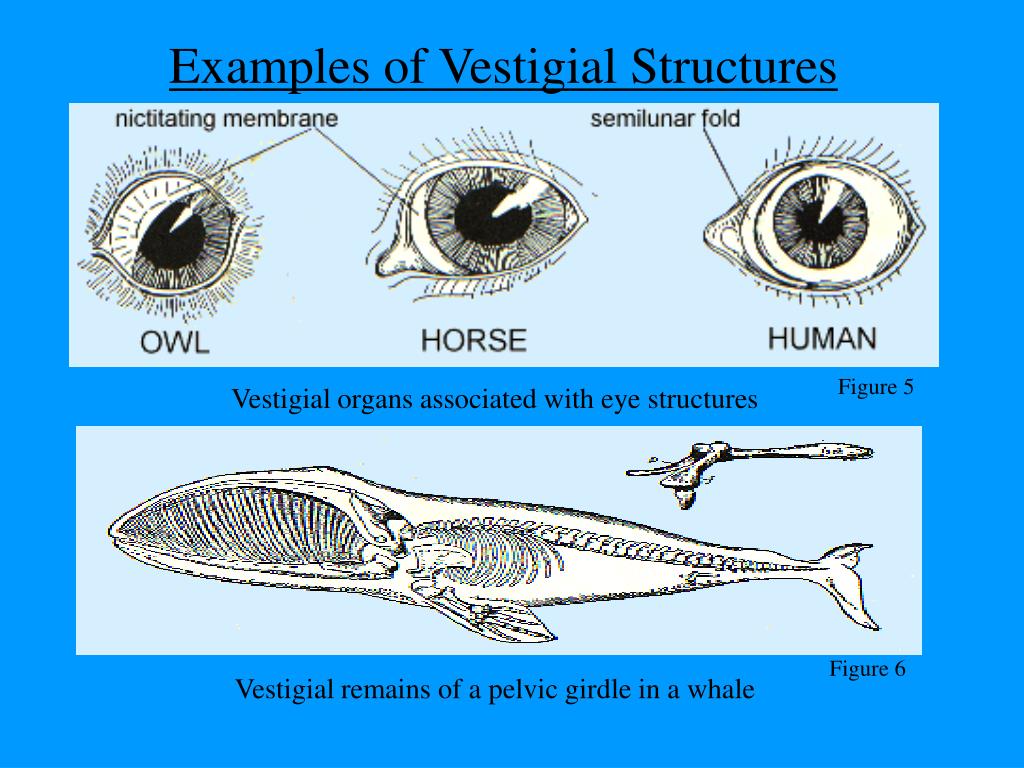
In simple words, the comparison of similarities and differences in the body structure of living organisms to trace evolutionary relationships with their ancestors. What is Comparative Anatomy?ĭefinition of comparative anatomy: This is the study of similar and different structures in organisms. Comparing and finding prehistoric relationships between ancestors and descendants based on their body structure is the most basic and important step in tracing evolution. You must've seen animals with the same body structures as we have. Scientists have come so far by understanding the concept of evolution that organisms undergo for their survival. But why do they do that? They are in search of a common ancestor, of course. Scientists always try to find more and more evolutionary relationships between species.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
